Document Service API: Middlewares
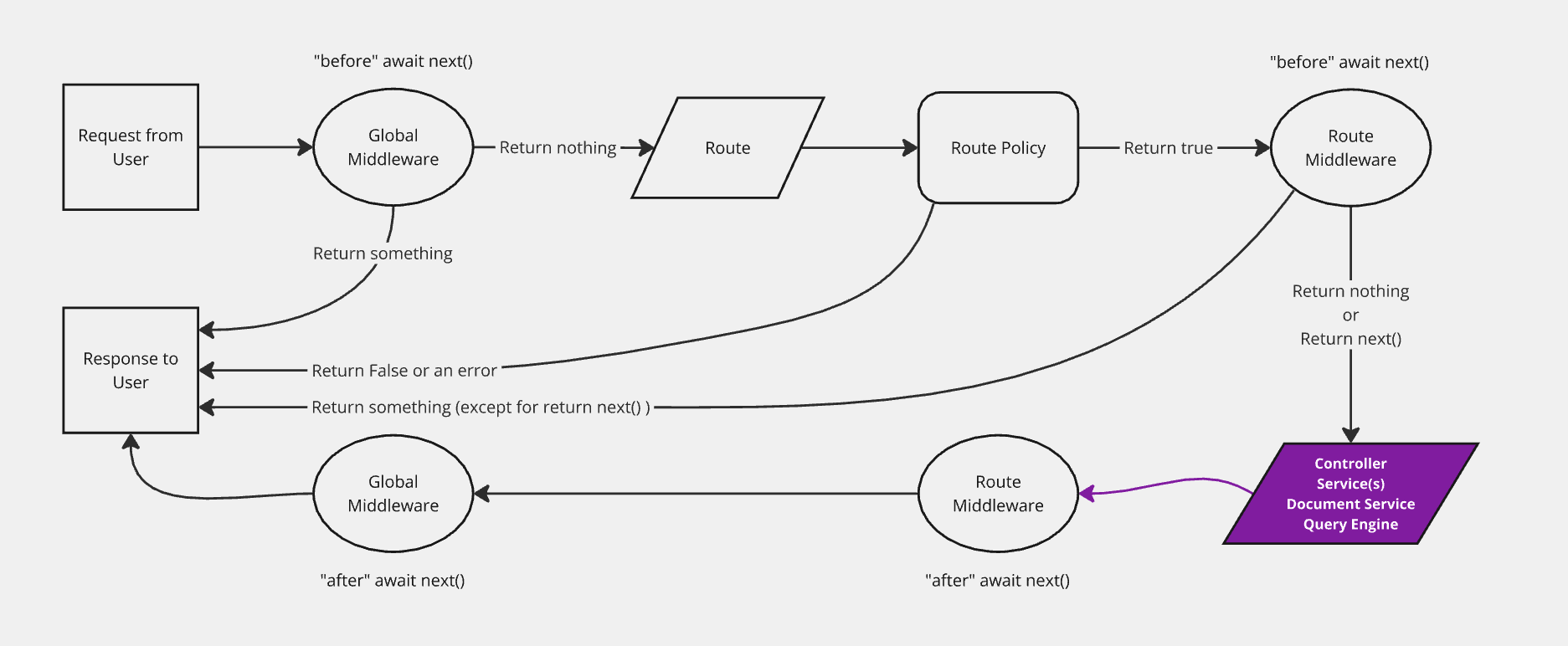
The Document Service API offers the ability to extend its behavior thanks to middlewares.
Document Service middlewares allow you to perform actions before and/or after a method runs.
Registering a middleware
Syntax: strapi.documents.use(middleware)
Parameters
A middleware is a function that receives a context and a next function.
Syntax: (context, next) => ReturnType<typeof next>
| Parameter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
context | Middleware context | Context |
next | Call the next middleware in the stack | function |
context
| Parameter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
action | The method that is running (see available methods) | string |
params | The method params (see available methods) | Object |
uid | Content type unique identifier | string |
contentType | Content type | ContentType |
next
next is a function without parameters that calls the next middleware in the stack and return its response.
Example
strapi.documents.use((context, next) => {
return next();
});
Where to register
Generaly speaking you should register your middlewares during the Strapi registration phase.
Users
The middleware must be registered in the general register() lifecycle method:
module.exports = {
register({ strapi }) {
strapi.documents.use((context, next) => {
// your logic
return next();
});
},
// bootstrap({ strapi }) {},
// destroy({ strapi }) {},
};
Plugin developers
The middleware must be registered in the plugin's register() lifecycle method:
module.exports = {
register({ strapi }) {
strapi.documents.use((context, next) => {
// your logic
return next();
});
},
// bootstrap({ strapi }) {},
// destroy({ strapi }) {},
};
Implementing a middleware
When implementing a middleware, always return the response from next().
Failing to do this will break the Strapi application.
Examples
const applyTo = ['api::article.article'];
strapi.documents.use((context, next) => {
// Only run for certain content types
if (!applyTo.includes(context.uid)) {
return next();
}
// Only run for certain actions
if (['create', 'update'].includes(context.action)) {
context.params.data.fullName = `${context.params.data.firstName} ${context.params.data.lastName}`;
}
const result = await next();
// do something with the result before returning it
return result
});
The Document Service API triggers various database lifecycle hooks based on which method is called. For a complete reference, see Document Service API: Lifecycle hooks.